7 Thriving Careers in Cybersecurity: Unlocking a Future Full of Opportunities
In today’s rapidly advancing digital world, cybersecurity has become more critical than ever before. With increasing threats to data, privacy, and infrastructure, organizations are scrambling to protect their systems and networks. This demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals has opened up a wide range of career opportunities for those looking to enter the field. If you’re considering a career change or are just starting out, now is the perfect time to explore the diverse paths within cybersecurity. Let’s take a closer look at seven thriving careers in cybersecurity and how they can unlock a future full of opportunities.
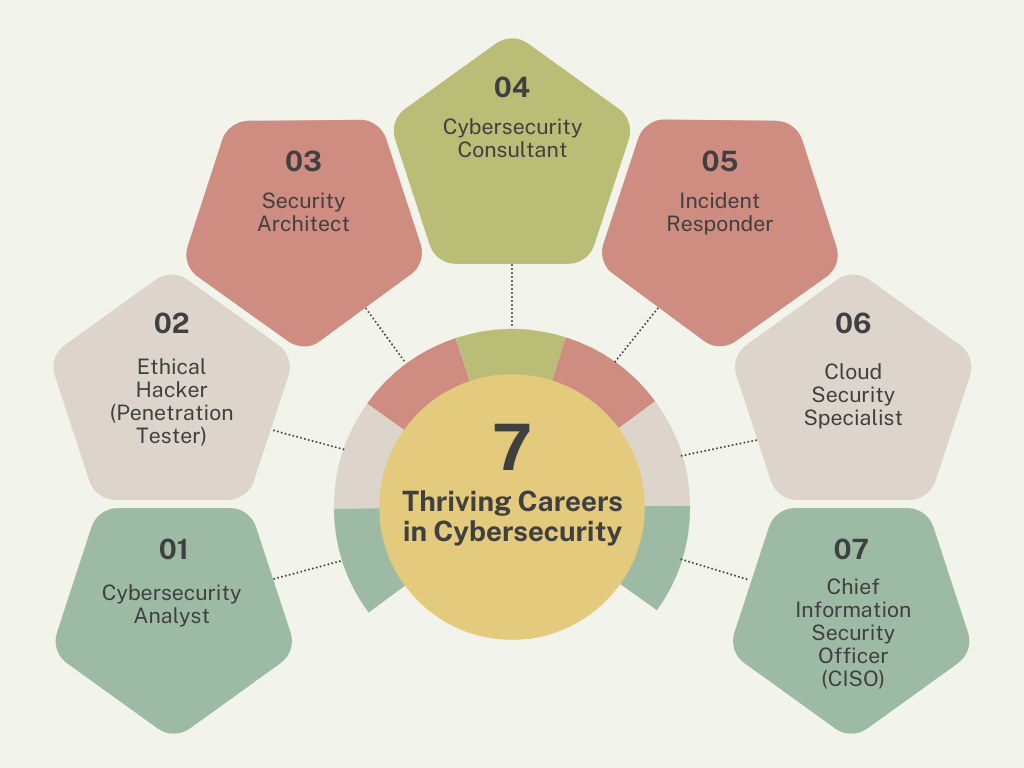
1. Cybersecurity Analyst
As organizations continue to face cyberattacks, the role of a cybersecurity analyst is in high demand. Cybersecurity analysts are responsible for monitoring an organization’s network and systems for any signs of vulnerabilities or breaches. They use various tools to identify potential threats and respond to security incidents. The job requires a deep understanding of network security, encryption methods, and risk assessment.
Why it’s thriving: With the increase in cyber threats, businesses are investing heavily in cybersecurity defense, making this one of the most stable and high-demand careers in the tech industry.
Skills Required:
- Knowledge of firewalls, IDS/IPS, and SIEM tools
- Familiarity with network protocols and encryption
- Understanding of threat intelligence
2. Ethical Hacker (Penetration Tester)
Ethical hackers, also known as penetration testers, are cybersecurity professionals who are hired to identify vulnerabilities in systems by attempting to hack them. Unlike malicious hackers, ethical hackers work within the law to help organizations identify and patch weaknesses before they are exploited by cybercriminals. This role requires creative thinking and an in-depth understanding of how attackers exploit systems.
Why it’s thriving: As companies shift towards proactive security measures, the need for ethical hackers to test their systems is growing. The constant arms race between attackers and defenders ensures that ethical hackers will remain in high demand.
Skills Required:
- Proficiency in programming languages like Python, C, or JavaScript
- Experience with penetration testing tools (e.g., Kali Linux, Metasploit)
- Knowledge of web application security and networking
3. Security Architect
Security architects are responsible for designing, building, and maintaining secure systems for organizations. They analyze an organization’s infrastructure and create comprehensive security frameworks to ensure that sensitive data remains protected. This role involves strategic planning, selecting security tools, and overseeing the implementation of security protocols across the organization.
Why it’s thriving: With businesses investing heavily in cybersecurity, security architects play a crucial role in shaping the security infrastructure from the ground up. Their expertise ensures that organizations are equipped to handle future cyber threats.
Skills Required:
- Expertise in firewalls, VPNs, encryption, and multi-factor authentication
- Knowledge of regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA)
- Strong leadership and project management skills
4. Cybersecurity Consultant
Cybersecurity consultants work as external advisors to help organizations improve their security posture. They conduct risk assessments, audit systems, and recommend solutions to mitigate vulnerabilities. Consultants often work for consulting firms or as independent contractors, providing specialized advice to various industries, including healthcare, finance, and government.
Why it’s thriving: Many businesses lack the in-house expertise to handle cybersecurity challenges, leading them to turn to consultants for guidance. As cybersecurity threats grow, the demand for specialized consultants continues to rise.
Skills Required:
- Strong knowledge of cybersecurity frameworks and compliance standards
- Experience in risk management and incident response
- Excellent communication skills to advise clients effectively
5. Incident Responder
Incident responders are the first line of defense when a cyberattack occurs. They are responsible for managing and mitigating the impact of security breaches. This role involves identifying the cause of the attack, containing the damage, and working to restore systems to normal operations. Incident responders must act quickly and efficiently to minimize the consequences of an attack.
Why it’s thriving: As cyberattacks become more frequent and sophisticated, the demand for skilled incident responders continues to grow. Their expertise is critical in containing and resolving security incidents in real time.
Skills Required:
- Expertise in digital forensics and malware analysis
- Familiarity with incident response frameworks (e.g., NIST)
- Ability to work under pressure and in high-stress situations
6. Cloud Security Specialist
As organizations increasingly move their operations to the cloud, the need for cloud security specialists has surged. These professionals ensure that cloud infrastructures, applications, and data are secure from potential threats. Cloud security specialists focus on encryption, identity management, and access control to ensure that cloud environments remain safe and compliant with industry regulations.
Why it’s thriving: The shift to cloud computing has created new security challenges, and businesses require experts who understand how to secure cloud-based environments. Cloud security specialists are essential in safeguarding cloud data and applications.
Skills Required:
- Knowledge of cloud platforms (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Experience with cloud security best practices and tools
- Understanding of cloud compliance standards (e.g., SOC 2, ISO 27001)
7. Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is a senior executive responsible for overseeing the cybersecurity strategy of an entire organization. The CISO is in charge of managing the cybersecurity team, aligning security goals with business objectives, and ensuring that security policies and procedures are implemented across the organization. They are the key decision-maker when it comes to mitigating risk and safeguarding sensitive data.
Why it’s thriving: As cyber threats become more complex, organizations are placing more emphasis on leadership in cybersecurity. The role of CISO is integral to ensuring that security initiatives are effective and aligned with overall business goals.
Skills Required:
- Extensive experience in cybersecurity and risk management
- Strong leadership and strategic thinking abilities
- In-depth knowledge of cybersecurity regulations and policies
Conclusion
The field of cybersecurity offers a wide variety of career opportunities for those interested in protecting digital infrastructures from threats. Whether you’re drawn to technical roles like ethical hacking and penetration testing or leadership positions like a CISO, there’s a career path for everyone in cybersecurity. With the ever-growing threat landscape, cybersecurity professionals will continue to be in high demand, making it a stable and rewarding career choice. By developing the right skills and gaining relevant experience, you can unlock a future full of opportunities in this thriving and vital industry.