Biometric Authentication in Cybersecurity
In the rapidly advancing landscape of cybersecurity, staying one step ahead of malicious actors is a constant challenge. Traditional methods of password protection are proving to be increasingly vulnerable, leading to a growing interest in more sophisticated and secure alternatives. One such groundbreaking solution gaining prominence is biometric authentication.

The Rise of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication marks a paradigm shift in how we secure our digital assets. Unlike conventional password-based systems, biometric authentication relies on unique physical or behavioral attributes to verify and grant access. This cutting-edge technology is a game-changer in the realm of cybersecurity, offering a more secure and user-friendly alternative.
Understanding Fingerprint Authentication
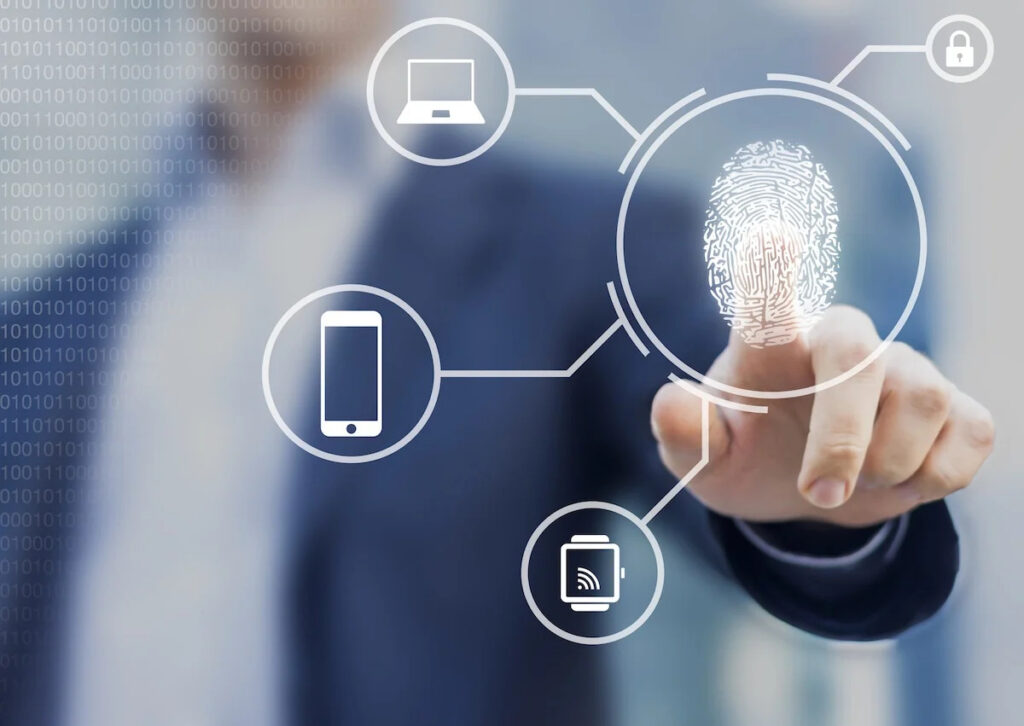
Among the myriad forms of biometric authentication, fingerprint authentication stands out as a frontrunner. Leveraging the distinctive patterns on an individual’s fingertips, this method provides a robust and efficient means of identity verification. As each person’s fingerprint is unique, the chances of unauthorized access are significantly minimized.
The Mechanism Behind Fingerprint Authentication
The process involves capturing an individual’s fingerprint through a sensor and converting it into a digital template. This template is then stored securely and used as a reference point for subsequent authentication attempts. The uniqueness and permanence of fingerprints make them an ideal biometric marker, and advancements in technology have made fingerprint scanners more accurate and reliable than ever.
Biometric Verification: A Multifaceted Approach
Beyond fingerprints, the world of biometric verification encompasses an array of modalities. Facial recognition, voice recognition, iris scans, and even behavioral traits like typing patterns are being explored to create a multi-layered defense against unauthorized access. This diversity ensures that even if one biometric modality is compromised, others provide an additional layer of security.
The Human Touch in Biometric Verification
One of the key advantages of biometric verification lies in its human-centric approach. By utilizing unique physical attributes or behaviors, it adds a personal touch to security. Users are not burdened with the task of remembering complex passwords, and the risk of unauthorized access due to stolen or weak passwords is virtually eliminated.
Overcoming Challenges: Addressing Concerns and Risks
While biometric authentication offers a promising future for cybersecurity, it is not without its challenges. Concerns related to privacy, the potential for spoofing, and the storage of biometric data have been raised. Striking the right balance between convenience and security is crucial, and ongoing research and development aim to address these issues.
Privacy Concerns
One of the primary concerns associated with biometric authentication is the potential invasion of privacy. Collecting and storing sensitive biometric data raise questions about how securely this information is stored and who has access to it. To mitigate these concerns, rigorous privacy regulations and standards are being developed to govern the collection, storage, and usage of biometric data.
Spoofing and Anti-Spoofing Measures
Biometric systems are not immune to spoofing attempts where attackers try to replicate biometric features to gain unauthorized access. In the case of fingerprint authentication, for example, there have been instances of creating fake fingerprints using various materials. To counteract this, continuous advancements in anti-spoofing technologies, such as liveness detection, are being implemented to ensure that the biometric data captured is from a live and authentic source.
Secure Storage of Biometric Data
The secure storage of biometric data is a critical aspect of the overall security framework. Biometric templates must be stored in a highly encrypted and tamper-resistant manner. Moreover, there is a growing trend towards decentralized storage solutions, ensuring that even if one database is compromised, the entirety of the biometric database is not at risk.
The Future of Cybersecurity: A Biometric Horizon
As technology continues to evolve, the future of biometric authentication appears bright. Advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence are contributing to more sophisticated algorithms, making biometric systems even more accurate and resistant to fraudulent attempts. Moreover, the integration of biometrics with other authentication factors is on the horizon, creating a comprehensive security framework.
Multi-Factor Authentication
The future of biometric authentication lies in its integration with other forms of authentication, creating a multi-factor authentication (MFA) approach. Combining biometrics with traditional factors like passwords or PINs enhances overall security by requiring attackers to compromise multiple layers of authentication. This layered approach adds an extra level of protection against unauthorized access.
Continuous Authentication
Traditional authentication methods often require a user to authenticate only at the initial login. However, the future may see the implementation of continuous authentication, where the system consistently monitors biometric traits throughout a user’s session. If any irregularities or anomalies are detected, the system can prompt for reauthentication, preventing unauthorized access even after the initial login.
In Conclusion:
In conclusion, biometric authentication is reshaping the cybersecurity landscape by providing a secure and user-friendly alternative to traditional password-based systems. Fingerprint authentication, as a subset of biometrics, is leading the way in ensuring robust identity verification. As the technology matures and addresses current challenges, the future promises a more secure digital environment where individuals can access their information with confidence, knowing that their unique biometric markers are safeguarding their digital identity. With ongoing research and development, the biometric horizon holds the key to a cybersecurity landscape that is not only more secure but also more user-centric and efficient.