Cyber Threat Intelligence Career Guide 2025: Skills, Roles, and Opportunities
In today’s hyperconnected world, cybersecurity is no longer an optional investment but a critical necessity for organizations across industries. Among the myriad roles in the cybersecurity domain, one that has garnered increasing attention is Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI). This specialized field combines elements of research, data analysis, and strategic decision-making to proactively combat cyber threats. Whether you are a seasoned professional looking to specialize or a newcomer intrigued by the intersection of technology and intelligence, understanding a career in CTI can open up exciting opportunities.
What is Cyber Threat Intelligence?
Cyber Threat Intelligence refers to the process of gathering, analyzing, and utilizing data about potential or current threats to an organization’s digital infrastructure. It involves identifying threat actors, understanding their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), and predicting future attacks to strengthen an organization’s security posture.
CTI is not just about identifying malware or stopping phishing attacks; it’s about developing actionable insights that can help organizations make informed security decisions. These insights often come from analyzing a combination of open-source intelligence (OSINT), technical threat data, human intelligence (HUMINT), and dark web reconnaissance.
Key Responsibilities of a Cyber Threat Intelligence Professional
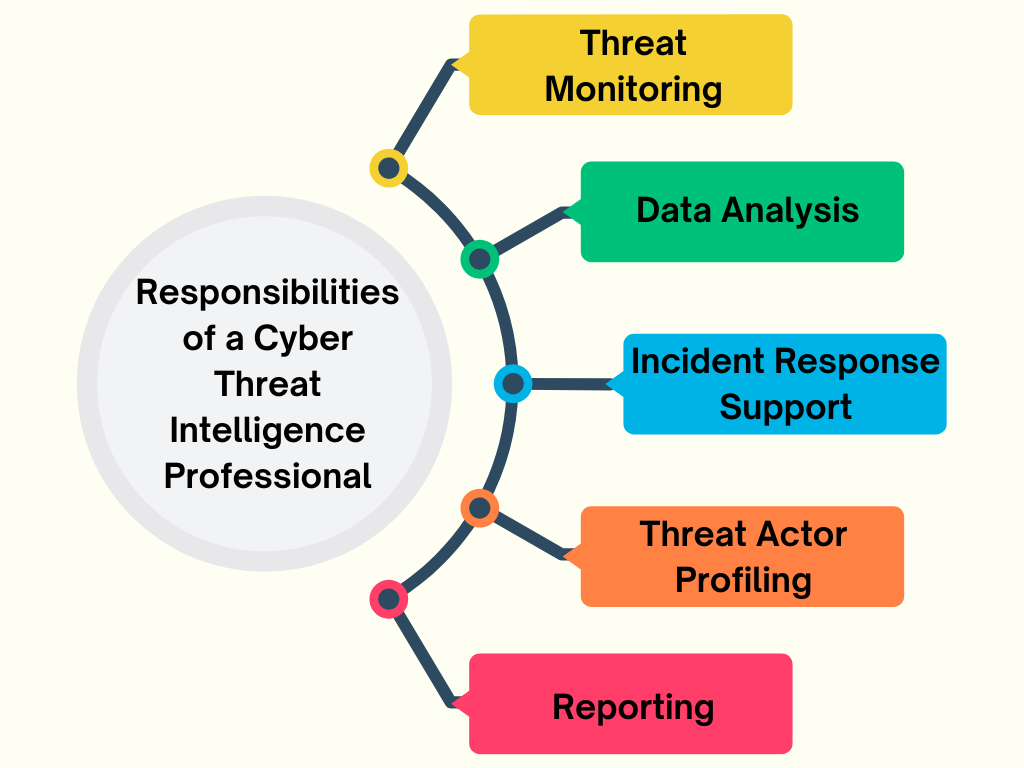
- Threat Monitoring: Continuously tracking emerging cyber threats, vulnerabilities, and trends.
- Data Analysis: Collecting and interpreting data from diverse sources, including malware reports, logs, and threat feeds.
- Incident Response Support: Collaborating with incident response teams to provide context and intelligence on ongoing threats.
- Threat Actor Profiling: Identifying and profiling cybercriminal groups to anticipate their actions.
- Reporting: Creating detailed reports and briefings for stakeholders, translating technical findings into actionable strategies.
Skills Required for a Career in CTI
To excel in Cyber Threat Intelligence, a combination of technical expertise, analytical skills, and soft skills is essential. Key competencies include:
- Technical Knowledge:
- Understanding of networking protocols, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
- Familiarity with malware analysis, reverse engineering, and forensic techniques.
- Analytical Skills:
- Ability to identify patterns in complex datasets.
- Proficiency in tools like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems and threat intelligence platforms.
- Communication Skills:
- Writing clear and concise intelligence reports.
- Communicating technical findings to non-technical stakeholders.
- Critical Thinking:
- Assessing the credibility of sources and prioritizing threats based on their relevance.
- Strategic thinking to anticipate threat trends.
- Continuous Learning:
- Staying updated on the latest cybersecurity trends and technologies.
Career Pathways in Cyber Threat Intelligence
Cyber Threat Intelligence professionals can follow various career trajectories, often starting in entry-level roles and progressing to specialized or leadership positions. Common roles include:
- Threat Analyst: An entry-level position focusing on monitoring and analyzing threat data.
- Threat Intelligence Researcher: Specializing in deep-dive research into threat actors and their methodologies.
- CTI Manager: Overseeing intelligence operations and ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
- CTI Consultant: Advising multiple organizations on developing and enhancing their CTI capabilities.
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): Leveraging intelligence insights to guide an organization’s overarching cybersecurity strategy.
Tools and Technologies Used in CTI
Professionals in CTI rely on a range of tools and platforms to gather and analyze data. Some of the most commonly used tools include:
- Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs): Recorded Future, ThreatConnect, Anomali.
- Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) Tools: Maltego, Shodan, SpiderFoot.
- Malware Analysis Tools: Cuckoo Sandbox, VirusTotal.
- Network Analysis Tools: Wireshark, Zeek.
- Dark Web Monitoring Tools: Tor Browser, DarkOwl.
Why Pursue a Career in Cyber Threat Intelligence?
The growing sophistication and volume of cyber threats make CTI a highly rewarding and impactful career choice. Here are some compelling reasons to consider this field:
- High Demand: As organizations recognize the value of proactive threat intelligence, the demand for skilled CTI professionals is skyrocketing.
- Dynamic Work Environment: No two days are the same in CTI, as professionals constantly tackle new challenges and evolving threats.
- Competitive Salaries: According to industry reports, CTI roles offer lucrative compensation packages, often exceeding the median salary for IT professionals.
- Opportunity to Make an Impact: By preventing cyberattacks, CTI professionals play a vital role in protecting sensitive data and maintaining public trust.
- Diverse Career Options: With applications in government, finance, healthcare, and more, CTI offers diverse opportunities for specialization.
Challenges in Cyber Threat Intelligence
While CTI is a promising field, it is not without its challenges:
- Information Overload: Managing and filtering vast amounts of threat data can be daunting.
- Rapidly Evolving Threats: Staying ahead of ever-changing attack vectors requires constant vigilance and adaptability.
- Collaboration Across Teams: CTI often involves working with multiple stakeholders, which can lead to communication gaps.
- High-Stress Environment: The stakes are high, and quick decision-making is often required to mitigate threats.
How to Get Started in CTI
Breaking into the CTI field requires a combination of education, certifications, and hands-on experience. Here’s how you can begin:
- Educational Background: A degree in cybersecurity, computer science, or a related field provides a solid foundation.
- Certifications: Industry-recognized certifications like Certified Threat Intelligence Analyst (CTIA), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), or GIAC Cyber Threat Intelligence (GCTI) are valuable.
- Practical Experience: Internships, labs, and CTF (Capture The Flag) competitions can provide hands-on experience.
- Networking: Joining cybersecurity communities and attending conferences can help you build connections and learn from industry experts.
- Continuous Learning: Explore online courses, webinars, and threat intelligence reports to stay updated.
Future Trends in Cyber Threat Intelligence
The CTI field is evolving rapidly, with several trends shaping its future:
- AI and Machine Learning: Automating threat detection and analysis to improve efficiency.
- Collaboration Platforms: Enhanced sharing of threat intelligence across organizations and industries.
- Focus on Insider Threats: Developing strategies to mitigate risks from within organizations.
- Integration with Risk Management: Aligning CTI efforts with broader business risk management practices.
- Emerging Threats: Addressing challenges like IoT vulnerabilities and nation-state cyber activities.
Conclusion
A career in Cyber Threat Intelligence offers the perfect blend of technical expertise, strategic thinking, and meaningful impact. As the digital landscape grows increasingly complex, CTI professionals are at the forefront of protecting sensitive information and critical infrastructure. Whether you are drawn to the thrill of tracking threat actors or the satisfaction of preventing potential disasters, CTI provides a fulfilling and dynamic career path. With the right skills, dedication, and curiosity, you can make a significant contribution to this vital field.