How to Start with Cybercrime Investigation
In today’s tech-savvy world, where digital footprints are everywhere, the need for cybercrime investigators has never been greater. Cybercrimes, like hacking, identity theft, and online fraud, are on the rise and can have devastating consequences for individuals and businesses. So, how can you dive into the world of cybercrime investigation, even if you’re just starting out and don’t have a background in complex tech jargon?
In this beginner-friendly guide, we will unravel the secrets of cybercrime investigation in simple terms. We’ll walk you through the essential steps, tools, and skills needed to become a cybercrime investigator. Whether you’re a curious mind, a budding cybersecurity enthusiast, or someone considering a career change, this guide will provide you with a solid foundation to start your journey into the fascinating world of cybercrime investigation. Let’s get started with understanding the benefits of becoming a certified cyber criminologist. Let’s get started!
Understanding Cybercrime
What is Cybercrime?
At its core, cybercrime encompasses a wide range of illegal activities that leverage computer systems, networks, and the internet to cause harm, steal, or compromise data. These activities often exploit vulnerabilities in technology or manipulate human behavior to achieve malicious goals.
Common Examples of Cybercrime:
- Hacking: Hackers break into computer systems or networks to gain unauthorized access. They may steal sensitive information, disrupt operations, or compromise the security of a system.
- Phishing: Phishing attacks involve tricking individuals into revealing confidential information, such as login credentials or credit card details, by posing as trustworthy entities through deceptive emails or websites.
- Identity Theft: Cybercriminals can steal personal information to impersonate individuals, commit fraud, or engage in illegal activities on their behalf.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is malicious software that encrypts a victim’s data, rendering it inaccessible. Cybercriminals then demand a ransom for the decryption key.
- Malware: Malware, short for malicious software, includes viruses, worms, Trojans, and other software designed to harm or compromise computer systems.
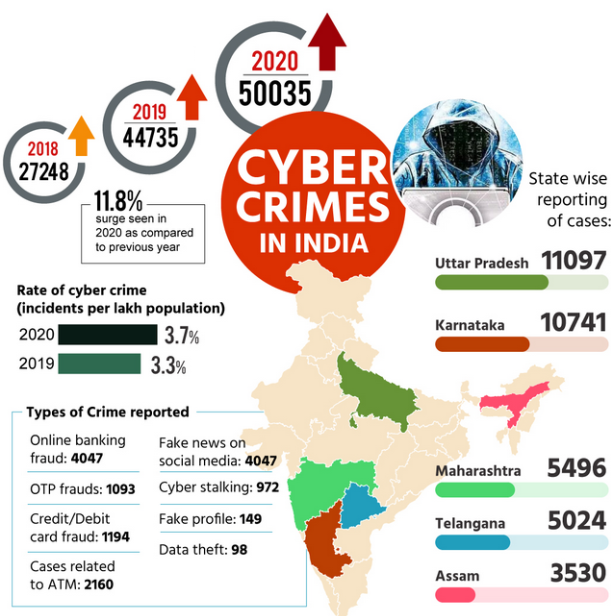
Global impact of cybercrime
Skills Required for Cybercrime Investigation:
Skills Required for Cybercrime Investigation: Becoming a proficient cybercrime investigator requires a broad range of skills and knowledge. It’s not just about understanding the basics; it’s about being well-equipped to tackle the ever-evolving challenges of the digital realm.
Here, we’ll discuss the areas you should focus on to become a competent cybercrime investigator, including cyber criminology certification programs, cybersecurity and criminology certification, and more. Whether you’re looking to start a career in this field or enhance your existing skills, the following modules provide a comprehensive roadmap.
- Foundations of Cybercrime: Gain insights into the world of cybercrimes and their far-reaching consequences.
- Building Investigative Skills: Equip yourself with the skills for gathering and analyzing digital evidence.
- Data Analysis and Intelligence: Elevate your investigative game with advanced data analysis and intelligence techniques.
- Navigating Digital Frontiers: Explore the hidden world of the dark web and cryptocurrency investigations.
- Tackling Cyber Threats: Learn to counter social engineering attacks and outsmart cybercriminals.
- Digital Media Analysis: Master the art of analyzing digital content and unlisted communications.
- Financial Investigations: Dive into financial and fraud-related investigations, covering a range of crimes.
- Privacy and Sensitive Content: Address privacy concerns and handle cases involving sensitive content professionally.
- Surveillance and Digital Tracking: Discover the power of surveillance, tracking, and digital forensics.
- Advanced Intelligence: Elevate your intelligence-gathering and evidence-mapping skills to expert levels.
Exploring these modules in depth, you can find more information about our comprehensive cybercrime investigation course here
As you embark on your journey to become a cybercrime investigator, keep in mind the career prospects for certified cyber criminologists. You’ll be contributing to a safer, more secure digital world for individuals, businesses, and nations alike. Your dedication to unraveling digital mysteries and pursuing justice will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of cybersecurity.
Some Frequently Asked Questions
What does a cybercrime investigator do?
A cybercrime investigator tracks down and catches cybercriminals involved in activities like hacking and identity theft. They collect digital evidence and work with law enforcement to bring criminals to justice.
What qualifications do I need to become a cybercrime investigator?
While there are no strict requirements, a background in computer science or cybersecurity can help. Many investigators earn certifications in these fields to boost their skills and job prospects.
Why is a cyber criminology certification important?
Cyber criminology certifications offer specialized training in digital forensics and cyber threat detection. They validate your expertise and can improve your chances of a successful career in cybercrime investigation.
How do investigators handle cases involving the dark web and cryptocurrency?
Investigators are trained to navigate the dark web and conduct cryptocurrency investigations. They learn to track digital transactions and gather evidence for cases involving these hidden online areas.
What job opportunities exist for certified cyber criminologists?
Certified cyber criminologists can work for law enforcement, cybersecurity firms, government agencies, and more. They can hold roles such as cybercrime investigator, digital forensics analyst, or cybersecurity consultant. The demand for these professionals is high due to the rise in cybercrimes.