Importance of Digital Forensics In Cybersecurity
WHAT IS DIGITAL FORENSIC ?
Digital forensics, also known as digital forensic science or computer forensics, is a branch of forensic science encompassing the recovery, investigation, and analysis of digital data found on electronic devices and digital storage media. Digital forensic experts collect and preserve digital evidence in a manner that maintains its integrity and ensures it can be used effectively.
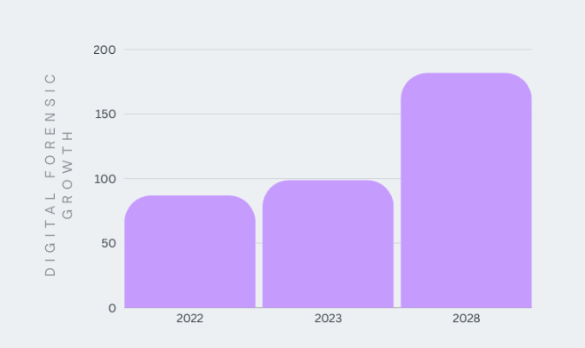
Digital forensics is critical in cybersecurity as it enables organizations to respond effectively to security incidents, mitigate risks, and recover from cyberattacks. The global digital forensic market is expected to be worth USD 18.2 Billion by 2028.
OBJECTIVES OF DIGITAL FORENSICS IN CYBERSECURITY
The objectives of digital forensics in cybersecurity are to facilitate swift and effective incident response by identifying security breaches promptly. It aims to collect and preserve digital evidence in a forensically sound manner, enabling thorough investigation and analysis to understand the nature and scope of incidents. Digital forensics also plays a crucial role in determining the identity and motives of attackers, which informs cybersecurity defences against specific threats. Additionally, it contributes to improving overall security posture by identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in systems and procedures, thereby enhancing resilience against future cyber threats. Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, ensuring business continuity, and minimising the impact of incidents on operations are also key objectives, making digital forensics integral to comprehensive cybersecurity strategies.
Overall, the objectives of digital forensics in cybersecurity are to support proactive measures to prevent incidents, provide effective response capabilities when incidents occur, and ensure that organisations can recover quickly and learn from each incident to improve their overall cybersecurity resilience.
TYPES OF DIGITAL FORENSICS
Importance of digital forensics in cyber security is due to its role in investigating, analysing, and mitigating cyber incidents. In today’s interconnected digital landscape, where cyber threats are pervasive and sophisticated, digital forensics provides essential tools and methodologies to understand the nature and scope of attacks.
A few types of Digital forensics are described below. Each type focuses on specific aspects of digital investigations. Each type of digital forensics requires specialised knowledge, tools, and techniques tailored to the specific characteristics and challenges of the digital environment being investigated.
- Disk Forensics: Involves analysing data on physical storage devices like hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and USB drives to uncover evidence of illegal activity, unauthorised access, or other suspicious behaviour.
- Network Forensics: Focuses on monitoring and analysing network traffic and log data to investigate security incidents, identify attackers, and understand the extent of a cyber attack.
- Email Forensics: Investigates email headers, contents, attachments, and metadata to trace the origin of emails, verify their authenticity, and retrieve deleted or hidden messages.
- Cloud Forensics: Examines data stored in cloud environments to investigate security incidents, unauthorised access, or data breaches involving cloud services such as SaaS (Software as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service).
- IoT Forensics: Investigates Internet of Things (IoT) devices to retrieve evidence related to cybercrimes, including data breaches, unauthorised access, and device manipulation.
DIGITAL FORENSIC TOOLS
Digital forensic tools are software and hardware solutions used to collect, preserve, analyse, and present digital evidence for legal purposes. These tools are crucial in investigating cybercrimes, data breaches, and other digital incidents.
These tools are crucial for efficiently handling and processing large volumes of data while maintaining the integrity of evidence. Here are some common categories and examples of digital forensic tools
- Computer Forensics: It is also known as digital forensics, it involves the investigation of digital devices like computers, servers, and storage media to uncover evidence related to crimes or incidents. Computer forensics examines file systems, operating systems, applications, and network traffic to extract and analyse data.
- Network Forensics: This branch deals with monitoring and analysing network traffic and activities to identify security incidents, unauthorised access, or suspicious behaviour. Network forensics tools capture and analyse packets to reconstruct events and determine the scope and impact of security breaches
- Database Forensics: Database forensics focuses on investigating database systems to recover and analyse data, identify unauthorised access, detect data breaches, or investigate fraud. It involves examining database logs, tables, queries, and metadata for evidence.
- Memory Forensics: Memory forensics involves analysing the volatile memory (RAM) of a computer or device to extract artefacts such as running processes, network connections, encryption keys, and other data that may not be stored on disk. This is crucial for investigating live system intrusions or malware.
- Malware Forensics: Malware forensics deals with analysing malicious software (malware) to understand its behaviour, origins, and impact on systems. Investigators examine malware samples, code, execution traces, and network communications to determine how malware operates and its potential impact.
- Cloud Forensics: With the increasing use of cloud computing services, cloud forensics involves investigating data stored on cloud platforms. Investigators analyse cloud storage, logs, access records, and virtual machine snapshots to recover evidence or investigate incidents involving cloud-based services.
ROLE OF DIGITAL FORENSIC SPECIALIST
A digital forensic specialist plays a critical role in the field of cybersecurity and investigative procedures by applying specialised knowledge and techniques to analyse and interpret digital evidence.
Firstly, in incident response, a digital forensic specialist is instrumental in quickly identifying the nature and extent of cybersecurity incidents, such as data breaches or malware attacks. They employ rigorous methodologies to collect and preserve digital evidence from affected systems, ensuring that all findings adhere to legal standards and maintain integrity. This approach not only aids in understanding how attackers gained access and what actions they performed but also guides organisations in effectively containing and mitigating the impact of the incident.
Secondly, in legal proceedings, digital forensic specialists play a pivotal role in providing expert testimony and presenting their findings in a clear and understandable manner to stakeholders, including law enforcement, legal teams, and organisational leadership. Their ability to reconstruct digital timelines, recover deleted or encrypted data, and analyse network traffic patterns often forms the basis for building strong cases against cybercriminals or supporting defence strategies in litigation.
Furthermore, digital forensic specialists contribute to enhancing overall cybersecurity posture by conducting proactive investigations and vulnerability assessments. By identifying weaknesses in systems, policies, or practices, they help organisations implement preventive measures and improve incident response preparedness. This proactive approach not only mitigates future risks but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and resilience against evolving cyber threats.
DIGITAL FORENSIC PROCESS
The role of digital forensics in cybersecurity is to recover, investigate and analyse the data. The digital forensic process involves a systematic approach to gathering, preserving, analysing, and presenting digital evidence in a manner that maintains its integrity and admissibility. While specific methodologies may vary depending on the nature of the investigation and the tools used, the general digital forensic process typically includes the following key steps:
- Identification: The process begins with identifying and defining the scope of the investigation. This involves determining the nature of the incident or crime, understanding the objectives of the investigation, and identifying the digital devices or systems involved.
- Preservation: Once identified, the next step is to preserve the integrity of potential evidence. This includes using write-blocking techniques or tools to prevent accidental modification or contamination of digital evidence during the collection process. Physical access controls and chain of custody procedures are also established to maintain the integrity of evidence.
- Collection: Digital evidence is collected from relevant sources such as computers, mobile devices, servers, and network logs. This may involve creating forensic copies (bit-by-bit images) of storage media using specialised tools like FTK Imager, EnCase, or dd. Live system data may also be captured using forensically sound methods to analyse volatile memory (RAM) or running processes.
- Examination: Once collected, the forensic examiner analyses the digital evidence using various techniques and tools. File system analysis helps in identifying files, folders, and metadata, while keyword searches and data carving tools are used to recover deleted or obscured data. Network traffic analysis tools like Wireshark are employed to reconstruct communication patterns and identify potential unauthorised activities.
- Analysis: In-depth analysis of the recovered digital artefacts is conducted to reconstruct events, establish timelines, and determine the relevance of evidence to the investigation. This may involve correlating findings across multiple sources, identifying relationships between entities (e.g., users, files, network nodes), and validating the integrity and authenticity of evidence.
CONCLUSION
Moreover, digital forensics plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity measures, enabling organisations to fortify defences, mitigate risks, and respond effectively to breaches. It supports regulatory compliance efforts by ensuring that investigative practices adhere to legal standards, thereby bolstering trust and confidence in digital transactions and communications. Digital forensics continues to evolve as a cornerstone of cybersecurity strategy and criminal investigation, safeguarding digital assets, protecting individuals’ rights, and upholding the principles of accountability and due process in our increasingly interconnected world.