The Impact of Cryptocurrency on Cybercrime
WHAT IS CRYPTOCURRENCY ?
Cryptocurrency is a digital form of currency that uses cryptography for security and operates independently of a central authority, such as a government or financial institution. Bitcoin and other types of cryptocurrencies have exploded onto the market in recent years, and based on virtual currency’s popularity, it seems to be here to stay. It is decentralised and typically based on blockchain technology, a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers.
Key characteristics of cryptocurrencies include:
- Decentralisation: Cryptocurrencies are typically decentralised, meaning they are not controlled by any single entity or government. Instead, they operate on a peer-to-peer network of computers (nodes) that collectively validate and record transactions.
- Cryptography: Cryptocurrencies use cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. This ensures the integrity and security of transactions and helps prevent fraud and counterfeiting.
- Blockchain Technology: Most cryptocurrencies rely on blockchain technology, which is a distributed ledger that maintains a continuously growing list of records (blocks) linked and secured using cryptography.
- Digital Nature: Cryptocurrencies exist purely in digital form and do not have physical counterparts like coins or banknotes. They are stored in digital wallets, which are secured with private keys that provide access to the funds.
- Global Accessibility: Cryptocurrencies enable fast and relatively low-cost peer-to-peer transactions across borders without the need for intermediaries like banks or payment processors. This can promote financial inclusion, especially in regions with limited access to traditional banking services.
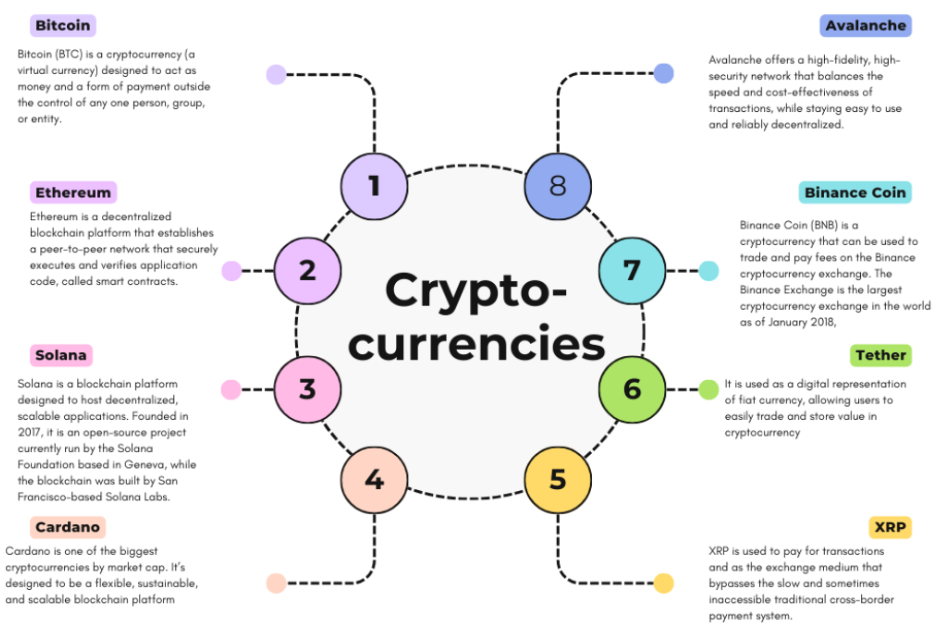
A few cryptocurrencies are explained below :
Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most famous cryptocurrency, created by an anonymous person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin is often referred to as digital gold and is used as a store of value and medium of exchange.
Ethereum (ETH): A decentralised platform that enables developers to build and deploy smart contracts and decentralised applications (dApps). Ether (ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum platform, used to pay for transaction fees and computational services on the network.
Polkadot (DOT): Developed by the Web3 Foundation, Polkadot is a multi-chain blockchain platform that enables interoperability between different blockchains. It aims to facilitate a decentralised internet where multiple blockchains can seamlessly interact.
HOW HAS CRYPTOCURRENCY AFFECTED CYBERSECURITY/CYBERCRIME ?
Cryptocurrencies have indeed facilitated certain negative impacts on cybercrime, contrary to my previous response. Here are some key ways in which cryptocurrencies have been associated with facilitating or exacerbating cybercrime:
- Anonymity and Pseudonymity: While anonymity can be a positive feature for privacy-conscious individuals, it also allows cybercriminals to conduct transactions without revealing their identities. This makes it challenging for law enforcement agencies to trace and prosecute perpetrators involved in various forms of cybercrime, such as hacking, ransomware attacks, and illegal online marketplaces.
- Ransomware Payments: Cryptocurrencies, especially Bitcoin, have become the preferred method of payment for ransomware attacks. This is because cryptocurrencies enable quick and relatively anonymous transactions, making it easier for cybercriminals to extort payments from victims without the risk of being easily traced.
- Illicit Transactions on the Dark Web: Cryptocurrencies are commonly used on the dark web for illicit activities, including drug trafficking, weapons sales, stolen data trading, and other illegal transactions. The decentralised and pseudonymous nature of cryptocurrencies makes them attractive for conducting such activities away from traditional regulatory oversight.
- Money Laundering: Cryptocurrencies have been exploited for money laundering purposes, where criminals convert illicit funds into cryptocurrencies to obfuscate the origins of the money. They can then convert these cryptocurrencies back into fiat currencies through unregulated exchanges or mixing services, making it difficult for authorities to track and trace the flow of illegal funds.
- Scams and Fraud: Cryptocurrencies have been associated with numerous scams and fraud schemes, including Ponzi schemes, fake initial coin offerings (ICOs), pump-and-dump schemes, and phishing attacks. These schemes take advantage of the relative newness and lack of regulatory clarity in the cryptocurrency space to defraud unsuspecting investors and users.
- Exchange Hacks: Cryptocurrency exchanges, where users trade and store their digital assets, have been frequent targets of cyberattacks. Hackers exploit vulnerabilities in exchange platforms to steal cryptocurrencies, resulting in significant financial losses for users and damaging trust in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
- Increased Cybercrime: The adoption of cryptocurrencies has also contributed to the increased sophistication of cybercrime tactics. Criminals leverage advanced techniques such as cryptojacking (using victims’ computing power to mine cryptocurrencies), ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS), and targeted phishing attacks that exploit the decentralised and global nature of cryptocurrency transactions.
FUTURE IMPACT OF CYBER RISKS ON CRYPTOCURRENCY
- Cryptojacking: Unauthorised use of devices to mine cryptocurrency
- Quantum computing threats: Potential future ability to break cryptographic algorithms
- Exchange hacks: Attacks on cryptocurrency exchanges to steal funds
- Wallet vulnerabilities: Exploits targeting software or hardware wallets
HOW TO STAY SAFE FROM CYBER CRIMES WHILE DEALING WITH CRYPTOCURRENCY ?
Cryptocurrencies have emerged as a revolutionary financial technology, providing new opportunities for decentralised transactions and secure digital assets. However, as the popularity of cryptocurrencies continues to grow, so does the risk of cyber-attacks and security breaches.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA on all your cryptocurrency exchange accounts and wallets to add an extra layer of security. This typically requires a second form of verification (e.g., a code sent to your mobile device) in addition to your password.
- Verify Website URLs: Be vigilant of phishing attacks where attackers create fake websites that mimic legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges or wallets. Always verify the URL of the website and ensure it uses HTTPS. Bookmark official websites and avoid clicking on links from unsolicited emails or messages.
- Backup Your Wallet: Regularly backup your wallet and keep multiple copies in secure, offline locations. This ensures you can recover your funds in case of device failure or loss.
- Be Sceptical of Investment Schemes: Exercise caution when investing in new cryptocurrencies or participating in initial coin offerings (ICOs). Research thoroughly and verify the legitimacy of projects and their teams before investing.
- Secure Your Private Keys: Your private keys are crucial for accessing and managing your cryptocurrency funds. Store them securely offline, preferably in a hardware wallet or a secure offline location. Avoid storing private keys on devices that are connected to the internet or are vulnerable to malware.
- Be Cautious with Public Wi-Fi: Avoid accessing your cryptocurrency accounts or making transactions using public Wi-Fi networks, as they may not be secure. Use a virtual private network (VPN) for added security when connecting to public Wi-Fi.
CONCLUSION
While cryptocurrencies themselves are not designed to promote cybercrime, their unique characteristics and the evolving landscape of digital finance have inadvertently created opportunities for exploitation by malicious actors. Its anonymous nature and large transaction capabilities have made it attractive to cybercriminals. Addressing these challenges requires a balanced approach that promotes innovation and financial inclusion while implementing robust cybersecurity measures and regulatory frameworks to mitigate risks associated with cryptocurrency-related cybercrime.