UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF ETHICAL AI IN CYBERSECURITY
WHAT IS ETHICAL AI ?
Ethical AI refers to the design, development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence systems that adhere to ethical principles and values. These principles aim to ensure that AI technologies are beneficial, fair, transparent, accountable, and aligned with human values and societal norms.
ETHICAL AI IN CYBERSECURITY
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in cybersecurity due to several compelling reasons
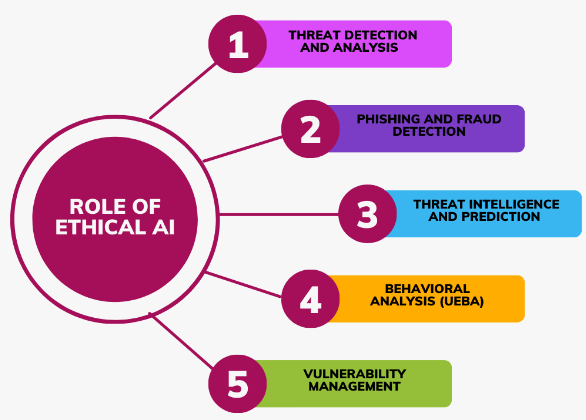
1. Threat Detection and Analysis:
- Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms can identify unusual patterns or behaviors within networks or systems that may indicate potential cyber threats. This includes detecting anomalies in user behavior, network traffic, or application usage.
- Pattern Recognition: AI can analyze large volumes of data to identify known attack patterns and signatures, helping to quickly recognize and respond to familiar threats.
2. Phishing and Fraud Detection:
- Email Analysis: AI algorithms analyze email content, headers, and sender behavior to detect phishing attempts and malicious attachments.
- User Behavior Analytics: AI can monitor and analyze user behavior to detect anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity or compromised accounts.
3. Threat Intelligence and Prediction:
- Predictive Analytics: AI models can analyze historical data and current trends to predict future cyber threats and vulnerabilities. This proactive approach helps organizations prepare and implement preemptive security measures.
4. Behavioral Analysis:
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): AI monitors and analyzes user interactions with IT systems to detect deviations from normal behavior, such as unauthorized access attempts or unusual data access patterns.
5. Vulnerability Management:
- Automated Patching: AI can prioritize and automate the application of software patches based on risk assessment and potential impact, reducing vulnerabilities and improving overall system security.
- Vulnerability Scanning: AI-driven vulnerability scanners can continuously monitor systems for potential weaknesses and recommend mitigation strategies.
BIASSING IN AI ALGORITHMS
Bias in AI within cybersecurity contexts can manifest in several ways, potentially leading to significant consequences if not properly addressed. Addressing bias in AI within cybersecurity is essential to ensure that AI technologies contribute positively to security efforts without inadvertently perpetuating or amplifying existing biases. By promoting fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI development and deployment, organizations can enhance the effectiveness and ethical integrity of their cybersecurity strategies. Here are some key aspects of bias in AI in cybersecurity
- Bias in Training Data:
- Imbalanced Data: Training datasets used to develop AI models may be biased towards certain demographics, regions, or types of cyber threats. This can result in AI systems that are less effective at detecting or responding to threats targeting underrepresented groups or uncommon attack vectors.
- Historical Bias: Data collected from past incidents may reflect biases present in human decisions and actions, which can be inadvertently perpetuated by AI algorithms. For example, if past incidents were disproportionately investigated in certain contexts, the AI may learn to prioritize those contexts over others.
- Algorithmic Bias:
- Biased Decision-Making: AI algorithms may exhibit bias in their decision-making processes, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. In cybersecurity, this could mean certain individuals or groups are more likely to be flagged as threats or targeted for monitoring based on biased patterns learned from historical data.
- Feature Selection Bias: The features or attributes considered by AI models may inadvertently encode biases present in the training data, affecting the accuracy and fairness of predictions.
- Impact on Security Operations:
- False Positives/Negatives: Bias in AI can lead to higher rates of false positives (flagging benign activities as threats) or false negatives (failing to detect actual threats), potentially undermining the effectiveness of cybersecurity defenses.
- Misallocation of Resources: Biased AI may allocate resources unevenly, focusing more on perceived threats to certain groups or environments while neglecting others that may actually be at higher risk.
- Ethical and Legal Implications:
- Discrimination and Privacy Concerns: Biased AI systems can inadvertently contribute to discrimination against individuals or groups, raising ethical concerns and potentially violating privacy rights if biased decisions lead to unfair treatment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations deploying AI in cybersecurity must navigate regulatory frameworks that prohibit discriminatory practices, requiring careful consideration of bias mitigation strategies.
- Mitigating Bias in AI in Cybersecurity:
- Diverse and Representative Data: Ensuring that training data used for AI models is diverse and representative of all relevant populations and contexts can help mitigate bias.
- Bias Detection and Evaluation: Implementing rigorous testing and evaluation frameworks to detect and mitigate bias in AI algorithms before deployment is critical.
- Regular Monitoring and Auditing: Continuously monitoring AI systems in production and conducting regular audits can help identify and address bias that may emerge over time.
RISKS IN ETHICAL AI
Spotting potential ethical AI and cybersecurity concerns is pivotal to effectively countering them. Once these risks are identified, it becomes essential to devise robust mitigation strategies. By employing comprehensive methods such as data governance combined with continuous cybersecurity monitoring, the inherent risks associated with these technologies can be significantly curtailed, fostering a safer digital environment.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, AI is transforming cybersecurity by enabling faster threat detection, more effective incident response, proactive vulnerability management, and adaptive security measures. As cyber threats continue to evolve in complexity and frequency, AI-driven solutions are increasingly essential to safeguarding organizations’ digital assets and maintaining robust cybersecurity postures. As cyber threats become more sophisticated and frequent, AI-powered solutions are increasingly essential to protect organizations’ digital assets and sensitive information effectively.